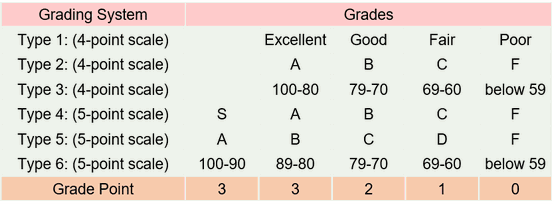
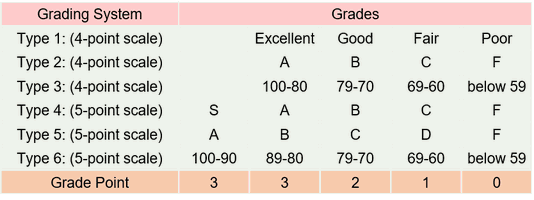
Masters programme is generally two years and doctoral programme is about three years for completion.
In some, doctoral programme may be composed of two years masters programme (First half of the doctoral program) followed by three years called "Last half of the doctoral program".
This is not the case for 6 years long medical, dental and veterinary undergraduate programme and 6 years long veterinary undergraduate programme. Both of which does not include master's
programme. Doctoral program for these may take four years.
Start of academic year is either Spring (April) or Fall (September or October).
*Just click each STEP for further information.
One of the following condition must be satisfied; as stated by
MEXT
Below is cited from
JASSO
In order to be admitted to Japanese universities or junior colleges, one the following conditions must be satisfied:
【For a Masters or the First Half of a Doctoral Program】
1. Individuals who graduated from a four-year university
2. Individuals who completed 16 years*1 of formal study in their country
*1 Medical, dental, pharmaceutical or veterinary students planning to enroll in a doctoral program must have completed at least 18 years of formal education
3. Individuals who completed at least 3 years of study at a foreign university and earned a bachelor's degree *Medical, dental, pharmaceutical or veterinary students planning to enroll in
a doctoral program must have completed at least 5 years of study
4. Individuals who were awarded a bachelor's degree from the National institution for Academic Degrees and Quality Enhancement of Higher Education
5. Individuals who completed 16 years of formal education in Japan via an online curriculum offered by a foreign school (18 years for medical, dental, pharmaceutical, or veterinary
students)
6. Individuals who completed their studies at a foreign school in Japan officially recognized as equivalent to that of a foreign university (according to MEXT's list of designated foreign
universities' with branch campuses in Japan)
7. Individuals who completed their studies at a designated vocational school (according to MEXT's list of designated vocational schools)
8. Individuals who completed their studies at a school under Japan's old education system
9. Individuals who completed their studies at the National Defense Academy of Japan, Japan Coast Guard Academy, Meteorological College, or another academy or college established by a
ministry or agency.
10. Individuals above the age of 22 who was accepted by the university based on the university's individual admission qualifications selection
【For the Second Half of the Doctoral Program】
1. Individuals who holds a Masters or professional degree
2. Individuals who holds a foreign degree equivalent to that of a Masters or professional degree
3. Individuals who earned a Masters or professional degree by completing an online curriculum at an overseas institution while residing in Japan
4. Individuals who completed their studies at a foreign school in Japan that is officially recognized as being equivalent to a foreign graduate school (according to MEXT's list of
designated foreign universities (graduate schools) with campuses in Japan)
5. Individuals who completed their studies at United Nations University and earned a degree equivalent to a Masters degree
6. Individuals who have obtained a Bachelor's degree or the equivalent and have completed at least 2 years at a university or research institute and possesses the same academic ability as
an individual who holds a Masters degree
7. Individuals aged 24 or above who were accepted by a graduate school based on the school's individual admission qualifications assessment
STEP 1 | Basic Eligibility
Look for a program in a university you wish to study for your graduate study.
Universities either provide programme/course in English or in the case of graduate study, if the prospective supervisor is able to give supervision in English, one can apply to the
graduate school.
Use the
data portal to find by what academic major you wish to pursue.
STEP 2 | Program and University Search
[PROSPECTIVE SUPERVISOR]
Applying to graduate school of your choice requires receiving prior consent from a professor to be your prospective supervisor. Some of the
universities require an applicant to directly contact the professor OR to contact through administration office of university. This is indicated in their university website or application
guideline.
Following are tips on how to prepare the essential document when contacting - the research proposal.
[RESEARCH PROPOSAL]
This is an outline of your research plan and methodology which will be an introductory document for professor to understand that you have a firm plan during your study in graduate school,
generally around 2000 words.
Content:
1) Purpose of research
2) Research background
3) Significance of the research
4) Research methodology
5) Bibliography
[APPLICATION DOCUMENTS]
Prepare the necessary documents as stated by each university in their APPLICATION GUIDELINE.
In case of graduate school, some will require one to apply as a "student" or to enroll after being a "research student".
Research student is as follows: (cited from JASSO)
A research student belongs to one of the following irregular/nontraditional student categories:
1. Individuals conducting short-term research who do not plan to obtain a degree (mostly graduate level)
2. Individuals participating in a short-term exchange program through an inter-university agreement (undergraduate or graduate)
3. Individuals participating in a university preparatory course as a prerequisite for enrollment in a graduate program (mostly individuals who completed their undergraduate studies)
Selection process: The selection process usually involves an assessment of application documents, but an interview is required in some cases.
Status of residence: Auditing students who are auditing all of their classes (not enrolled) must attend at least 10 hours of class per week in order to qualify for the "international
student" status. Research students who are not taking classes and are not receiving compensation for their research must have a "Cultural Activities" status of residence.
STEP 3 | Prospective Supervisor, Research Proposal and Application Documents
Selection process of graduate school differs by school. Most common procedures are combination of document assessment, academic skills test, interview, essay and oral examination.
STEP 4 | Entrance Examination
Once receiving the acceptance note for admission from your preferred university, first of all, congratulations! Now one can proceed to either;
1. Apply to scholarship or tuition waiver provided by university. This is in condition if the university you applied to has the system in place.
Often times, depending on your past academic record or performance upon application, university will determine whether he/she is eligible for tuition waiver. Some will waive up to
100%. Detail should be confirmed by the university you got accepted into.
2. Apply to scholarship provided by local government or foundation. There are several scholarships one can apply to once they have the acceptance note
from a university. Application procedure differ to apply directly to the scholarship by applicant or to apply via university you got accepted into.
STEP 5 | Apply to financial aid after receiving acceptance note
VISA
To study in Japan, one has to obtain "STUDENT VISA" from Japanese Embassy/Consulate at your residing country.
Detail can be found
here (external link to Japan Student Services Organization).
JAPANESE LANGUAGE
Even if the course you will enroll to is taught in English, it is always an advantage to know the local language in advance. Take your time to learn couple of helpful Japanese to start
your life in Japan. Options of courses can be found
here.
STEP 6 | Preparation for departure to Japan